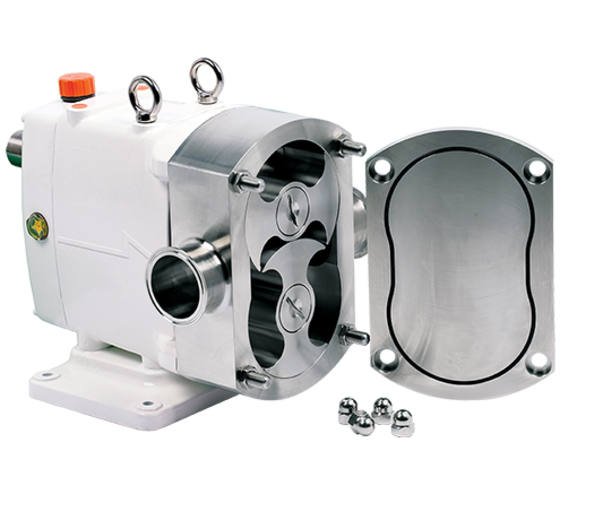

ZL
The Packo ZL series are designed for broad applications spectrum covering dairies, foods, beverages, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, bakeries, detergents, liquors and...
| Max. flow | 100 m3/h |
| Max. discharge pressure | 20 bar |

Discover the capabilities of these rotary positive displacement pumps
and how they can be the right solution for your application.
Do you have questions about our range?
One of our pump experts is here to support you.
These pumps, also known as rotary lobe pumps, are a type of positive displacement pump well-suited for moving viscous fluids. Their efficiency increases with higher product viscosity. They are appreciated for flexibility, low pulsation, and the ability to handle both high- and low-viscosity media at variable speeds.
On this page, you’ll learn how the technology works, the operating principle, key applications, and the Packo range designed for demanding industries.
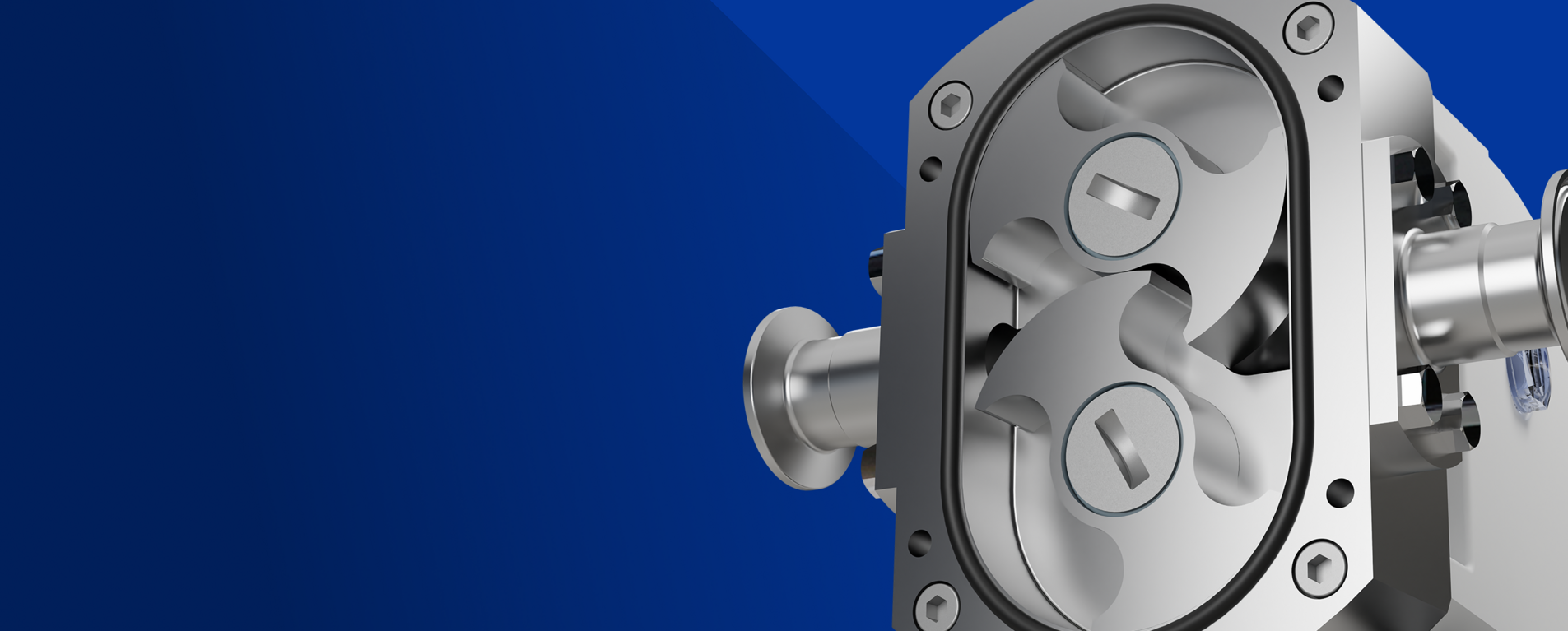
Operation is based on two lobes—similar to gears—rotating in opposite directions inside a casing. External timing gears keep them synchronized, maintaining a small clearance to avoid direct contact. This motion creates a vacuum that draws fluid in, traps it between the lobes and casing, and transfers it to the discharge side.
When the lobes mesh, the liquid is expelled from the pump. The following video demonstrates this process with a Packo HP/LH Hy~Line model.
Two counter-rotating rotors draw product into the pump chamber, fill the cavities, and move it around the casing to the discharge port. Different rotor designs; single, double, tri-lobe, multi-lobe, piston circumferential, or helical—can be selected to match the material and application.
Do you need help? Our pump experts are here to answer your questions!

The Packo ZL series are designed for broad applications spectrum covering dairies, foods, beverages, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, bakeries, detergents, liquors and...
| Max. flow | 100 m3/h |
| Max. discharge pressure | 20 bar |
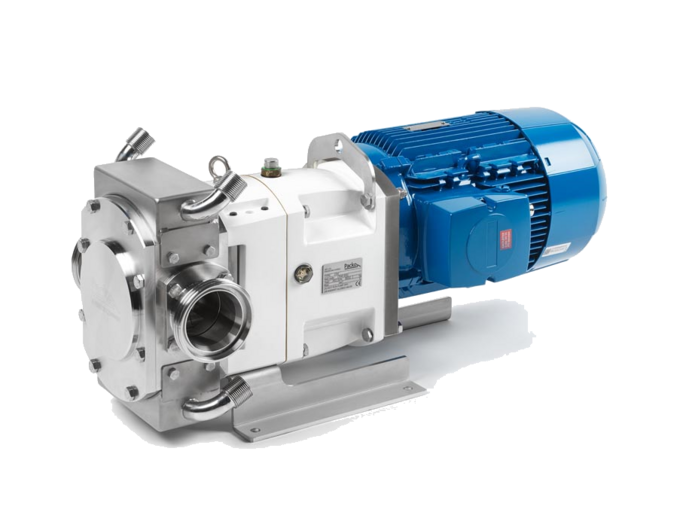
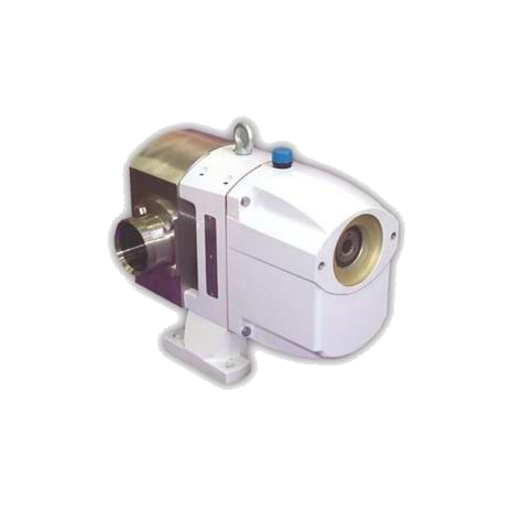
The LTE series is a high-quality, electrically driven hygienic truck pump designed for efficient loading and unloading of both low and high viscosity liquids. With its...
| Max. flow | 40 m3/h |
| Max. discharge pressure | 15 bar |

The Packo LT Series is a compact, hygienic rotary lobe pump designed for truck-mounted loading and unloading of low- to high-viscosity products, from thin liquids to...
| Max. flow | 40 m3/h |
| Max. discharge pressure | 15 bar |
Our lobe pumps are versatile and reliable solutions in handling viscous fluids. Some of the applications include:
Packo rotary lobe pumps are an investment in process reliability, hygiene, and efficiency. Benefits include: